What is breast cancer?
Discover what breast cancer is, the different types, the causes and more.
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is cancer found in the breasts or chest. It is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the breast.
Almost every cell in your body has DNA - a set of instructions that tell your cells when to grow and when to stop. But occasionally, a mutation occurs. Usually, it's harmless. But when mutations accumulate and don’t get fixed properly, they can make cells grow too fast, ignoring the body’s normal rules. When lots of these uncontrolled cells start to grow, it can form a tumour.
Just like many other cancers, that’s how breast cancer starts.
What is secondary breast cancer?
Secondary or metastatic breast cancer occurs when cancer cells have spread from the original breast tumor to other parts of the body, such as the bones, lungs, liver, or brain. It is also known as advanced or Stage 4 cancer. While secondary breast cancer cannot typically be cured, treatment aims to control the disease, slow its progression, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life.
Types of breast cancer.
Not all breast cancers are the same. They are often categorised based on where they start and how far they have spread.
Invasive Breast Cancer: This occurs when cancer cells have left the ducts or lobules and invaded the surrounding fatty tissue.
The most common form of breast cancers is:
- NST (No Special Type): The most common, formerly called invasive ductal carcinoma. Where cancer cells break through ducts into surrounding breast tissue (it accounts for around 70% of all invasive breast cancers).
- Invasive Lobular: Originates in milk-producing glands and spreads outward.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer: Rare, aggressive and causes redness, inflammation and swelling as the breast cancer cells block lymph vessels.
- Paget’s Disease of the Breast: Rare, causes change to the skin of the nipple and looks like eczema.
Non-invasive Breast Cancer: This is an early stage where cancer cells are still contained within the ducts or lobules and haven't spread to the surrounding tissue.
- DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma in Situ): Cancer cells are confined within ducts. If left untreated DCIS may become invasive.
- LCIS (Lobular Carcinoma in Situ): This type is not cancerous (so does not spread), although its presence is correlated with an increased chance of developing cancer.
Hormones and growth triggers.
Breast cancer can be broken down based on specific proteins and characteristics, such as whether it's fueled by hormones; oestrogen (ER+) and progesterone (PR+) or a protein called human epithelial growth factor 2 (HER2). This classification is crucial because it helps doctors choose the most effective treatment (for example lowering or blocking these hormones and proteins to help slow the growth of the tumour). About 80% of breast cancers have oestrogen receptors (ER+).
The most common markers are:
- ER+ / PR+ (hormone receptor-positive): Some breast cancer cells have special 'receptors' on their surface. When these hormones bind to the receptors, they can make the cancer cells grow and multiply. This means that the cancer’s growth is partly fueled by these hormones.
- HER2+: Some people have higher than normal levels of this protein which promotes tumour growth.
- Triple-Negative: No specific 'growth accelerators' like the known receptors or proteins, which means this type is often more aggressive and harder to treat. It is more common in younger women.
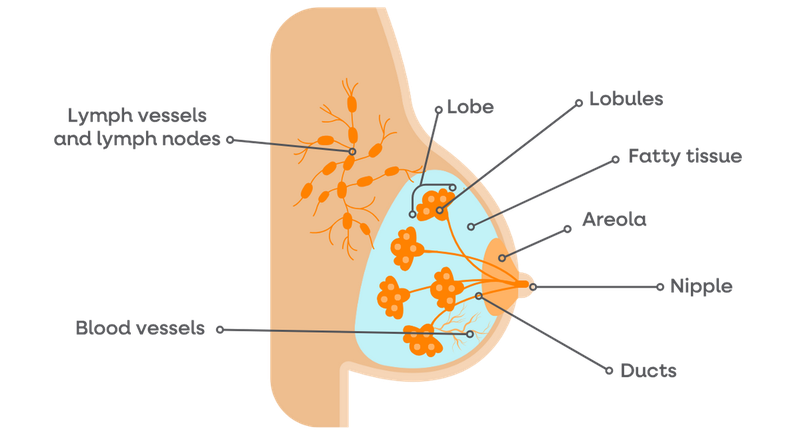
A closer look at breast anatomy.
The breast anatomy.
To understand breast cancer, it helps to know the parts of the breast.
- Lobules: Lobules are part of the glandular system; they are glands that produce breast milk.
- Ducts: Small tubes that carry breast milk from the lobules to the nipple.
- The nipple(s): Where breast ducts come together to allow for milk through a small opening in the skin.
- Fat and connective tissue: The supportive components that gives the breast its shape (they surround the ducts and lobules).
- Blood vessels: Allow for a constant supply of blood and nutrients to the breast to keep the tissue alive.
- Lymph vessels and lymph nodes: Part of the immune system that transport and filter lymph fluid. They function to help fight any infections away from the breast. In breast cancer, cancerous cells can enter the lymph vessels and start to grow in the lymph nodes. This is known as lymph node involvement.
Breast cancers are most often in the ducts (ductal cancers). Some breast cancers develop in the lobules (lobular cancers).
What causes breast cancer?
Breast cancer doesn't have a single cause. It's a complex disease influenced by a combination of factors. Understanding these factors helps us take proactive steps toward breast cancer prevention and early detection.
- Inherited risks: Genetics may influence your risk.
- Lifetime exposures: Higher concentrations of hormones like oestrogen can spur more cell divisions.
- Modern lifestyle and environment: Changes in how we live may increase risk.
In brief:
Understanding these basics isn’t just about science; it can empower you to spot meaningful changes early.
- Breast cancer happens when breast cells mutate and multiply uncontrollably.
- It often starts in ducts or lobules and may stay local or spread.
- Tumours are defined by their location, growth behaviour, and molecular markers.
- Hormones and proteins often help tumours grow (but can also guide treatment).
- Your breast cancer risk stems from many sources, from DNA to lifestyle.
Last review: Sept-25 | Next review: Sept-26.
-
{1} Cancer Research UK. Hormone therapy for breast cancer [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 7]. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/breast-cancer/treatment/hormone-therapy
{2} Cancer Research UK. Types of breast cancer and related breast conditions [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 7]. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/breast-cancer/types
{3} Kazuhiro I, Satoshi I. Estrogen receptors and their downstream targets in cancer. Arch Histol Cytol [Internet]. 2004 Dec [cited 2023 Aug 7];67(5):435–42. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15781984/
{4} Macmillan Cancer Support. Types of breast cancer [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 7]. Available from: https://www.macmillan.org.uk/cancer-information-and-support/breast-cancer/types-of-breast-cancer
{5} National Breast Cancer Foundation. Breast Cancer Anatomy & How Does Breast Cancer Start & Spread [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 7]. Available from: https://nbcf.org.au/about-breast-cancer/diagnosis/breast-cancer-anatomy/
{6} National Cancer Institute. What Is Cancer? [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 7]. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer
{7} Travis RC, Key TJ. Oestrogen exposure and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2023 Aug 7];5(5):239–47. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12927032/